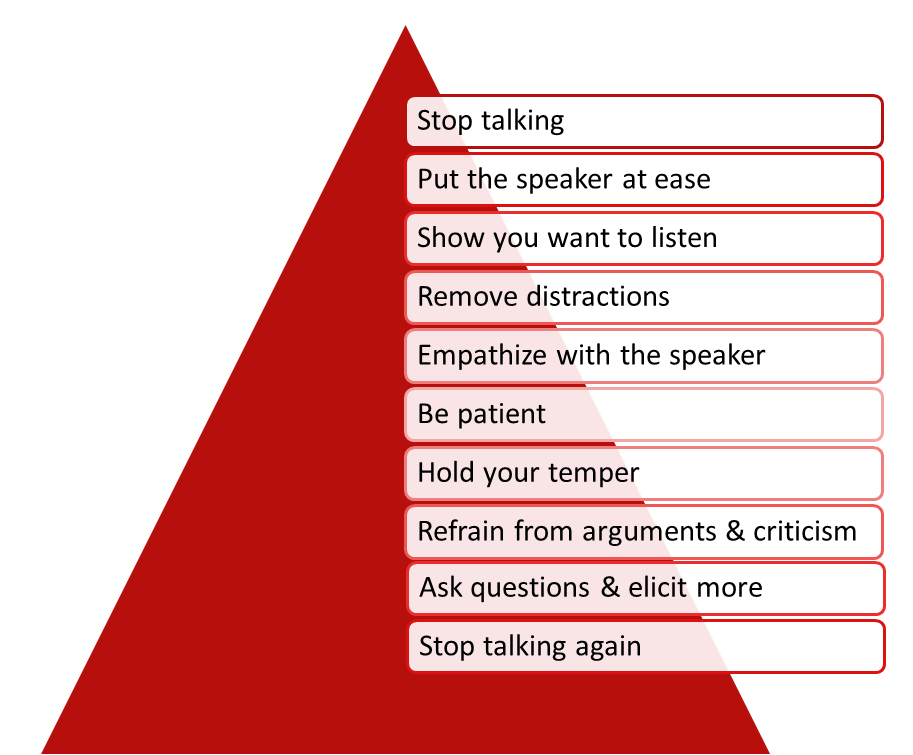
EFFECTIVE LISTENING 1.4
"Listening
is a skill while hearing
is
natural process."
Skills relating to Active Listening
•
Note-taking,
•
Effective Questioning & Paraphrasing
•
Non-verbal Communication
•
Semantic Markers
Note-taking
•
Note making vs. note taking.
•
Keeping a record for yourself
•
A selection and organization of words including the most important/
interesting parts of the lecture
•
Summarization and reflection on what they say.
•
Usage of a whole range of symbols,
abbreviations, our own form of shorthand
•
Identifying for oneself a list of key points
while revisiting the notes
Effective Questioning & Paraphrasing
•
One of the important skills within Active
Listening
•
To focus or concentrate more on what the speaker
is saying
•
Making a summary of what you heard
•
Closed questions vs. open-ended questions
•
Paraphrase to (i) Test your understanding of
what has been said, (ii) Demonstrate your understanding.
Non-verbal Communication (NVC)
•
Speech contains paralanguage, including voice
quality, emotion and speaking style
•
Written texts have nonverbal elements such as
handwriting style, spatial arrangement of words, or the use of emoticons
•
Posture & Gesture
•
Eye Contact is important.
Semantic Markers
• Noticing even the smallest aspects of communication such as semantic markers.
• The main ideas are cued with a facial expression and /or gesture and/ or phrases
note: Posture can be used to determine a participant’s degree of
attention or involvement, the difference in status between communicators, and
the level of fondness a person has for the other communicator. Posture is
understood through such indicators as direction of lean, body orientation, arm
position, and body openness. A gesture is a non-vocal bodily movement intended
to express meaning. Gestures may be articulated with the hands, arms or body,
and include movements of the head, face and eyes, such as winking, nodding, or
rolling ones’ eyes.
In short, good posture, paying attention to
speakers’ gestures and semantic markers and looking into the speaker’s eyes, facilitate and promote learning. Paying attention to
what your lecturer and/or speaker is saying and doing is key to success in your studies
and life.
to be continued...






No comments:
Post a Comment